Funky Boulder News
Your go-to source for the latest trends and stories in the vibrant world of culture and lifestyle.
RFID: The Invisible Thread Connecting Your World
Discover how RFID technology weaves a seamless web of connectivity, transforming everyday life. Unlock the secrets behind the invisible thread!
Understanding RFID: How It Works and Its Applications
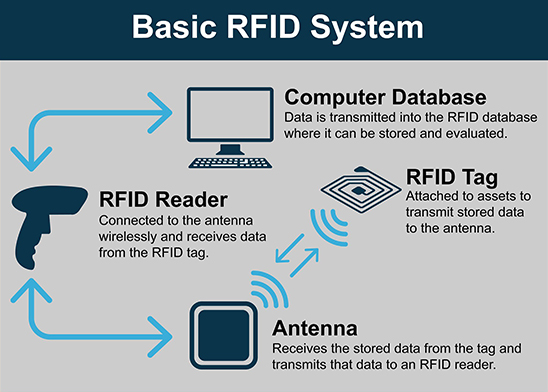
RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is a technology that utilizes electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system primarily consists of three components: the RFID tag, the RFID reader, and the backend database. The RFID tag contains a microchip with a radio antenna and can store a variety of information, while the RFID reader emits radio waves to communicate with the tag. When the tag enters the reader's field, it sends back the stored data. This process occurs instantly and without the need for line-of-sight, making RFID an efficient alternative to barcode scanning.
The applications of RFID technology are vast and continually expanding. Some prominent uses include:
- Inventory Management: Retailers utilize RFID to keep track of stock levels, thus improving accuracy and reducing loss.
- Supply Chain Tracking: Logistics companies employ RFID to monitor shipments and streamline their operations.
- Access Control: RFID is often used in security systems for door entry and authentication.
- Animal Tracking: Livestock and pets can be identified and monitored through embedded RFID tags.
This versatility demonstrates how RFID technology enhances efficiency across various sectors, leading to increased productivity and innovation.
Counter-Strike is a highly popular tactical first-person shooter game that emphasizes teamwork and strategy. Players participate in various objective-based game modes, often requiring them to work collaboratively to secure a win. For those looking for unique ways to organize their gaming accessories, check out the Top 10 airtag wallets that perfectly blend convenience with style.
The Future of RFID Technology: Trends and Innovations
The future of RFID technology is poised for significant transformation, driven by innovations across various industries. With the advent of more advanced chips and readers, RFID systems are becoming increasingly efficient, allowing for seamless inventory management and real-time tracking. Companies are exploring the integration of RFID with other technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), leading to more intelligent systems that provide deeper insights into operational processes.
As we look ahead, several key trends are expected to shape the deployment of RFID technology:
- Miniaturization of RFID tags will enable their use in smaller items and on a broader scale.
- Enhancements in data security will address privacy concerns, making RFID applications more appealing to consumers.
- Increased adoption in sectors such as healthcare and logistics will further drive innovation and cost reductions.
RFID vs. Barcodes: Which Technology Is Right for Your Business?
When it comes to inventory management and tracking, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and barcodes are two popular technologies that businesses often consider. RFID utilizes electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects, while barcodes rely on optical scanning to read printed codes. The choice between these technologies can significantly affect operational efficiency, inventory accuracy, and overall business performance.
Before making a decision, it's important to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each technology. For example, RFID allows for simultaneous scanning of multiple items without line-of-sight, which can save time in busy environments. On the other hand, barcodes are typically less expensive and easier to implement, making them suitable for smaller businesses or less complex systems. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on factors such as budget, industry requirements, and the scale of operations.